Hardware & Networking
.
 WORLDWIDE CONNECTIVITY -
WORLDWIDE CONNECTIVITY -
Worldwide network connectivity is an essential aspect of modern business and personal communication, as it enables individuals and organizations to connect and communicate with one another, no matter where they are located. At its core, worldwide network connectivity is made possible through a combination of various technologies, protocols, and infrastructure, all working together to facilitate communication and information exchange on a global scale.
One of the key technologies that enables worldwide network connectivity is the internet. The internet is a global network of computers and servers that are connected through a series of routers, switches, and other networking equipment. Through the internet, individuals and organizations can access a vast array of resources, including websites, email, cloud services, and more.
Another technology that plays a critical role in worldwide network connectivity is the Domain Name System (DNS). DNS is a system that translates domain names (such as www.example.com) into IP addresses (such as 192.0.2.1) that can be used to route traffic across the internet. By providing a human-readable way to access resources on the internet, DNS plays a key role in enabling worldwide connectivity.
Other technologies that enable worldwide network connectivity include networking protocols such as TCP/IP and HTTP, which facilitate the transmission and receipt of data across the internet. Infrastructure such as undersea fiber-optic cables and satellite networks also play a critical role in facilitating global connectivity, by providing high-speed data transfer capabilities across vast distances.
Overall, worldwide network connectivity is a complex and ever-evolving field that requires constant innovation and investment in technology and infrastructure. From the internet and DNS, to networking protocols and infrastructure, there are many components that must work together seamlessly to enable communication and information exchange on a global scale. As technology continues to advance, it's likely that we'll see even more exciting developments in the field of worldwide network connectivity, bringing people and organizations closer together than ever before.
 ASSET MANAGEMENT -
ASSET MANAGEMENT -
Asset management is the process of tracking and managing an organization's physical and digital assets. From IT equipment to office furniture and software licenses, asset management involves keeping track of what an organization owns, where those assets are located, and how they are being used. At its core, asset management is all about ensuring that an organization's assets are being utilized effectively, and that they are contributing to the success of the business.
From a technology standpoint, asset management involves using a range of software tools and systems to track and manage assets. These tools may include asset tracking software, inventory management systems, and asset management platforms. By using these tools, organizations can gain a clear view of their assets and how they are being used, enabling them to make informed decisions about when to replace or retire assets, as well as how to optimize their use.
One key benefit of asset management from a technology point of view is that it enables organizations to save time and reduce costs. By automating the tracking and management of assets, organizations can eliminate the need for manual processes such as spreadsheets and paperwork, which can be time-consuming and error-prone. This, in turn, can help to reduce the risk of lost or misplaced assets, as well as improve the accuracy of inventory management.
Another benefit of asset management from a technology point of view is that it can help organizations to better understand the total cost of ownership of their assets. By tracking the purchase price, maintenance costs, and other associated expenses, organizations can gain a clearer view of the financial impact of their assets over time. This, in turn, can help to inform decisions about when to retire or replace assets, and how to optimize asset utilization to maximize return on investment.
Overall, asset management is a critical process that can help organizations to optimize their use of physical and digital assets, reduce costs, and improve efficiency. From inventory management systems to asset tracking software and beyond, the use of technology is a key component of effective asset management, enabling organizations to gain a clear view of their assets and make informed decisions about how to best utilize them.
 HARDWARE EFFICIENCY & EXPANDABILITY -
HARDWARE EFFICIENCY & EXPANDABILITY -
Hardware efficiency and expandability are essential components of any modern technology infrastructure, and involve the use of advanced hardware and software systems to optimize performance and provide room for future growth. From a technology point of view, hardware efficiency and expandability involve the use of scalable hardware and software systems that can be expanded and upgraded as business needs evolve over time.
To provide hardware efficiency, businesses must first identify the hardware and software systems that are most critical to their operations, and then deploy the appropriate technologies to optimize their performance. This may involve the use of advanced hardware systems such as solid-state drives, high-performance processors, and large amounts of RAM to ensure that applications and systems run smoothly and efficiently.
At the same time, businesses must also ensure that their hardware systems are expandable and can be upgraded as needed to support future growth and changing business needs. This may involve the use of scalable server and storage systems that can be expanded as data volumes grow, or the use of virtualization technologies that allow businesses to easily scale their IT infrastructure as needed.
In addition to hardware efficiency and expandability, businesses must also focus on energy efficiency and sustainability. By deploying energy-efficient hardware systems and optimizing the use of power and cooling resources, businesses can reduce their carbon footprint and lower their operating costs over the long term.
Overall, hardware efficiency and expandability are critical components of any modern technology infrastructure, and require the use of advanced hardware and software systems to optimize performance and provide room for future growth. By focusing on scalability, energy efficiency, and sustainability, businesses can optimize their operations and drive greater efficiency, effectiveness, and success over the long term.
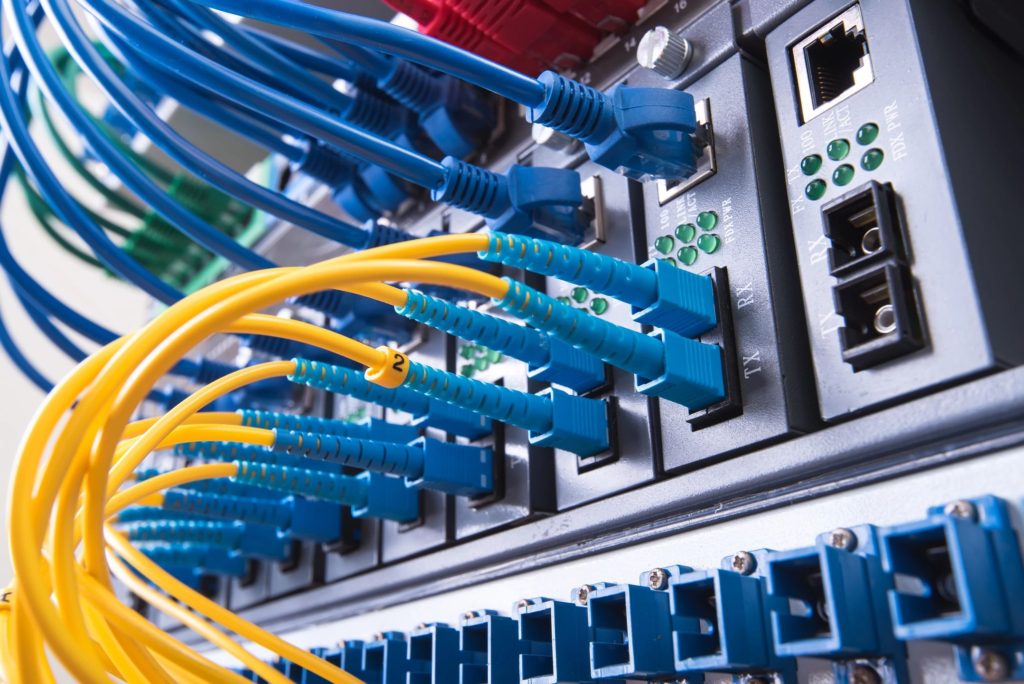 REDUNDANCY & DISASTER RECOVERY -
REDUNDANCY & DISASTER RECOVERY -
In the world of technology, redundancy and disaster recovery are two critical components of ensuring that business operations can continue uninterrupted in the event of an unexpected outage or disaster. From power outages to natural disasters and cyber-attacks, there are many potential threats that can disrupt business operations, making it essential to have a robust redundancy and disaster recovery plan in place.
At its core, redundancy refers to the practice of having multiple systems or components in place that can provide a backup in the event that a primary system or component fails. For example, a business may have multiple servers in different locations, so that if one server fails, another can take over its functions. Similarly, a business may use redundant power supplies or internet connections to ensure that critical systems can continue operating in the event of an outage.
Disaster recovery, on the other hand, refers to the process of recovering from an unexpected event that has disrupted business operations. This may involve restoring data from backups, replacing damaged hardware, or migrating operations to a backup site. A disaster recovery plan typically outlines the steps that will be taken in the event of a disaster, as well as the roles and responsibilities of key personnel.
From a technology standpoint, redundancy and disaster recovery require a range of tools and systems to be in place. This may include backup and recovery software, uninterruptible power supplies (UPS), redundant networking equipment, and more. It's also important to regularly test redundancy and disaster recovery systems to ensure that they are functioning properly and that the plan is effective.
Overall, redundancy and disaster recovery are critical components of any business's technology infrastructure. By implementing redundancy and disaster recovery systems and regularly testing them, organizations can help to ensure that their operations can continue uninterrupted, even in the face of unexpected events. With the right tools and planning in place, businesses can minimize the risk of downtime and data loss, and maintain the trust of their customers and stakeholders.



